Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Shimada, Taro; Nishimura, Yuki; Takeda, Seiji
MRS Advances (Internet), 2(12), p.687 - 692, 2017/01
A disposal measure for fuel debris generated at the accident in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station has been studied so far. However, physical and chemical properties of the fuel debris have not yet investigated in reactor containment vessels. In order to investigate the safety function of barriers required for disposal of fuel debris, sensitivity analyses for radionuclide migration were carried out, considering with uncertainty of the properties. As a result, it is indicated that it was important for evaluation of fuel debris disposal to obtain the physical and chemical properties of  C and
C and  I during release to groundwater, in addition to
I during release to groundwater, in addition to  U.
U.
Kitamura, Akira; Chikazawa, Takahiro*; Akahori, Kuniaki*; Tachi, Yukio
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 23(1), p.55 - 72, 2016/06
The Japanese geological disposal program has started researching disposal of spent nuclear fuel (SF) in deep geological strata (hereafter "direct disposal of SF") as an alternative management option other reprocessing followed by vitrification and geological disposal of high-level radioactive waste. We conducted literature survey of dissolution rate of SF matrix and constructing materials (e.g. zircaloy cladding and control rods) selected in safety assessment reports for direct disposal of SF in Europe and United States. We also investigated basis of release rate determination and assignment of uncertainties in the safety assessment reports. Furthermore, we summarized major conclusions proposed by some European projects governed by European Commission. It was found that determined release rates are fairly similar to each other due to use of similar literature data in all countries of interest. It was also found that the determined release rates were including conservativeness because it was difficult to assign uncertainties quantitatively. It is expected that these findings are useful as fundamental information for determination of the release rates for the safety assessment of Japanese SF disposal system.
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Bamba, Tsunetaka*; Hotta, Katsutoshi*; Mizuno, Tsuyoshi*; Ozawa, Tatsuya
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi, 4(4), p.242 - 247, 2005/12
no abstracts in English
Maeda, Toshikatsu; Bamba, Tsunetaka*; Mizuno, Tsuyoshi*
Haikibutsu Gakkai Rombunshi, 15(1), p.45 - 51, 2004/01
no abstracts in English
; Koyama, Tomozo; Funasaka, Hideyuki
JNC TN8400 2000-014, 78 Pages, 2000/03
We investigated the factors which affected the dissolution of U and Pu to the nitric acid solution with the fragmentation model, which was based on the results of dissolution experiments for the irradiated fast reactor fuels in the Chemical Processing Facility(CPF). The equation that gave the fuel dissolution rate was estimated with the condition of fabrication (Pu ratio (Pu/(U+Pu))), irradiation (burn-up) and dissolution (nitric acid concentration, solution temperature and U+Pu concentration) by evaluating these effects quantitatively. We also investigated the effects of fuel volume ratio to the solution in the dissolver, burn-up and flouring ratio of the fuel on the f-value (the parameter which shows the diffusion and osmosis of nitric acid to the fuel) in the fragmentation model. It was confirmed that the fuel dissolution rate calculated with this equation had better agreement with the results of dissolution experiments for the irradiated fast reactor fuels in the CPF than that estimated with the surface area model. In addition, the efficiency of this equation was recognized for the dissolution of unirradiated U pellet and high Pu enriched MOX fuel. It was shown that the dissolution rate of the fuel slowed down at the condition of the high U-Pu concentration dissolution by the calculation of the dissolution behavior with this equation. The dissolution of the fuel can be improved by increasing the nitric acid concentration and temperature, but from the viewpoint of lowering the corrosion of the dissolver materials, it is desirable that the f-value is increased by optimizing the condition of shearing and stirring for the improvement of dissolution.
Niimura, Nobuo; *; *
J. Jpn. Soc. Microgravity Appl., 15(SUPPL.2), p.582 - 584, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
; Sakai, Toshiyuki*; Sanyoshi, Hirotaka; Iwasaki, Isao*; Kuribayashi, Masakazu*;
PNC TN8410 95-056, 65 Pages, 1995/03
None
*
PNC TJ1211 95-007, 117 Pages, 1995/02
1. Survey on leaching rate of pyrite, chlorite, epidote and siderite. (1) Pyrite Reaction rate (K) is depended on dissolve O concentration in Lin's literature. 1 - (1-x)
concentration in Lin's literature. 1 - (1-x) 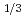 = k [O
= k [O ]
] 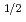 ・t (x: Mole number of dissolved FeS
・t (x: Mole number of dissolved FeS , [O
, [O ]: Dissolve O
]: Dissolve O concentration. T:Time) Reaction rate is changed by temperature. k = 2.2
concentration. T:Time) Reaction rate is changed by temperature. k = 2.2  10
10 exp(-9140/T) (2) chlorite Reaction rate is measured 2.7
exp(-9140/T) (2) chlorite Reaction rate is measured 2.7  6.7
6.7  10
10 mol/m
mol/m /s(pH3
/s(pH3  4.5) by Swoboda-Colberg et al. Reaction rate is controlled by inner diffusion. (3) Epidote Reaction rate is measured 10
4.5) by Swoboda-Colberg et al. Reaction rate is controlled by inner diffusion. (3) Epidote Reaction rate is measured 10
 10
10 mol/cm
mol/cm /s in pH1
/s in pH1  11 by Rose. (4) Siderite Reaction rate is measured 9.93
11 by Rose. (4) Siderite Reaction rate is measured 9.93  10
10 mol/m
mol/m /s in O
/s in O -free solution by Greenberg et al. 2. Experimental study on leaching rate of minerals. (1) Measurement of leaching rate of minerals. Leaching rate of pyrite was measured in distilled waster under redox condition. Reaction rate (K) was estimated 10
-free solution by Greenberg et al. 2. Experimental study on leaching rate of minerals. (1) Measurement of leaching rate of minerals. Leaching rate of pyrite was measured in distilled waster under redox condition. Reaction rate (K) was estimated 10
 10
10 (cm
(cm ・mol
・mol ) 1/2・h
) 1/2・h by Lin's rate equation. At 56 days in the experiments. Alterated layer could not be found in SEM and EDX observation. (2) Measurement of leaching rate of chlorite Leaching rate of chlorite was measured in distilled waster under air condition. Disolution process of chloric was parabolic Stage, and reaction rate (K) was estimated order of 10
by Lin's rate equation. At 56 days in the experiments. Alterated layer could not be found in SEM and EDX observation. (2) Measurement of leaching rate of chlorite Leaching rate of chlorite was measured in distilled waster under air condition. Disolution process of chloric was parabolic Stage, and reaction rate (K) was estimated order of 10
 10
10 by Ross's rate equation.
by Ross's rate equation. 
 = kt [
= kt [  : disoleved mineral amount / intial mineral amount, t : time(sec) ] At 56 days in the experiments, alterated layer could not be found in SEM and EDX observation.
: disoleved mineral amount / intial mineral amount, t : time(sec) ] At 56 days in the experiments, alterated layer could not be found in SEM and EDX observation.
Nemoto, Shinichi; Sakai, Toshiyuki*; Sanyoshi, Hirotaka; Kikuchi, Kenji; Iwasaki, Isao*; Kuribayashi, Masakazu*; Matsushima, Kazumi*
PNC TN8410 93-283, 86 Pages, 1993/11
None
Gonda, Kozo; Nemoto, Takeshi; Shibahara, Tetsuro
PNC TN841 79-06, 27 Pages, 1979/02
no abstracts in English
Sato, Tsutomu*; Oda, Chie
no journal, ,
Bentonite buffer and cement fluid interaction has been a key research issue in long-term safety assessment of radioactive waste disposal. The dissolution rate of smectite, the main constituent mineral of bentonite, has therefore been investigated under hyperalkaline conditions. A dissolution rate equation of smectite has been derived considering the effect of the Gibbs free energy of reaction and is applicable to pH = 7-13 and t = 25-80 C. Reactive-transport model analyses to elucidate the consequences of coupled changes in the porewater chemistry, mineralogy and, ultimately, the mass transport properties of the bentonite buffer were conducted using the smectite dissolution rate. Except in the close proximity of the cement interface, it was found that regardless of the choice of secondary minerals, the effective diffusion coefficient and hydraulic conductivity remained largely unchanged after 100,000 years.
C. Reactive-transport model analyses to elucidate the consequences of coupled changes in the porewater chemistry, mineralogy and, ultimately, the mass transport properties of the bentonite buffer were conducted using the smectite dissolution rate. Except in the close proximity of the cement interface, it was found that regardless of the choice of secondary minerals, the effective diffusion coefficient and hydraulic conductivity remained largely unchanged after 100,000 years.
 and spent fuel; A Review
and spent fuel; A ReviewKitamura, Akira; Akahori, Kuniaki*
no journal, ,
Since dissolution rate of UO matrices will be depend on carbonate concentration due to promoting oxidative dissolution of spent nuclear fuel by formation of carbonate complexes of uranium(VI), effect of carbonate concentration on dissolution rate of UO
matrices will be depend on carbonate concentration due to promoting oxidative dissolution of spent nuclear fuel by formation of carbonate complexes of uranium(VI), effect of carbonate concentration on dissolution rate of UO and spent nuclear fuel has been reviewed. It is found that a systematic study on dissolution rate of UO
and spent nuclear fuel has been reviewed. It is found that a systematic study on dissolution rate of UO and/or spent fuel as a function of carbonate concentration is recommended.
and/or spent fuel as a function of carbonate concentration is recommended.
 pellet
pelletMoroi, Yuriko*; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kitamura, Akira; Kimuro, Shingo
no journal, ,
Development of spent nuclear fuel direct disposal system is one of important options in Japan to maintain flexibility of the back-end strategy of nuclear fuel cycle. Other countries like Sweden and Finland advance in research and development of the direct disposal system. However, it is known that some groundwater in Japan contains higher concentration of carbonate ion than that in Sweden or Finland. Therefore, the effect of carbonate ion on the dissolution rate of UO has to be discussed to evaluate feasibility of the direct disposal system in Japan.
has to be discussed to evaluate feasibility of the direct disposal system in Japan.
 pellet
pelletMoroi, Yuriko*; Kirishima, Akira*; Akiyama, Daisuke*; Sato, Nobuaki*; Kitamura, Akira; Kimuro, Shingo
no journal, ,
Direct disposal of spent nuclear fuel is considered as an alternative option of geological disposal of high level radioactive wastes. In this case, the dissolution speed of uranium should be one of the most important parameter. In this study, the dissolution behavior of UO in the simulated groundwater contains high concentration of carbonate ion was investigated, then, it was revealed that uranium dissolution was promoted by the carbonate ion.
in the simulated groundwater contains high concentration of carbonate ion was investigated, then, it was revealed that uranium dissolution was promoted by the carbonate ion.